Sugar: The Silent Enemy of Your Oral Health
Sugar not only impacts weight but also poses a significant threat to oral health. When consumed in excess, bacteria in the mouth convert sugar into acid, which erodes enamel and creates the perfect environment for cavities to develop. Moreover, sugar contributes to gum inflammation and other serious dental diseases. So how can you protect your teeth from its harmful effects? Let’s explore this topic with The East Rose Dental Clinic in this article.
Why is sugar considered the silent enemy of oral health?

Sugar is a major contributor to dental damage because it creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive. When you consume sugary foods, bacteria in the mouth—especially Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus—ferment the sugar and produce lactic acid. This acid lowers the pH level in the mouth below neutral (around 5.5), triggering the demineralisation of tooth enamel. If this process continues unchecked, enamel erosion occurs, exposing the dentin and significantly increasing the risk of cavities.
Additionally, sugar reduces saliva production—an essential factor in neutralising acids and protecting teeth. Prolonged enamel damage significantly increases the risk of gum inflammation, periodontitis, and tooth loss. Therefore, it is crucial to regulate sugar intake in daily diets, as sugar is a true enemy of oral health.
The Harmful Effects of Sugar on Oral Health
Many people believe that sugar only impacts overall health and does not significantly affect oral health. However, excessive sugar consumption not only weakens tooth enamel but also creates ideal conditions for bacteria to thrive, leading to a range of serious dental and gum problems. Below are some concerning effects of sugar on oral health.
Causes Cavities and Enamel Erosion
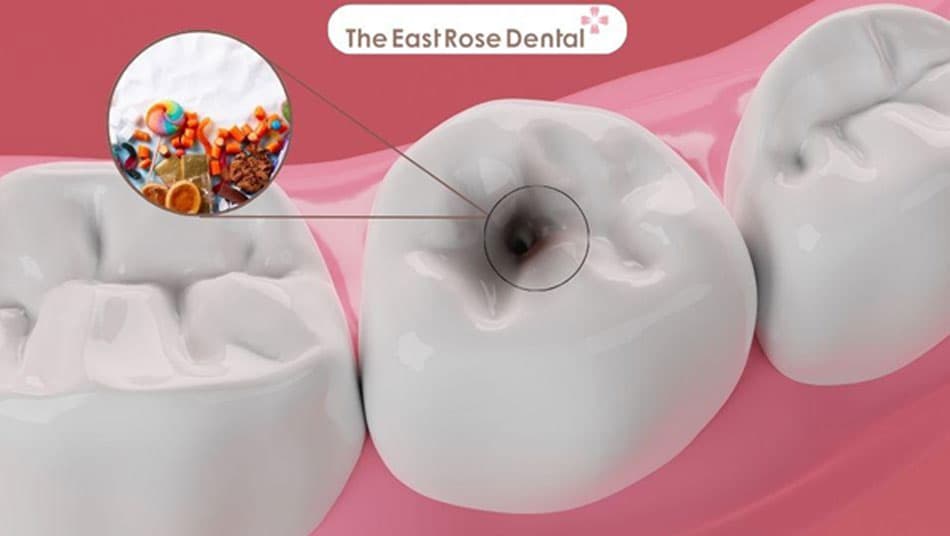
When sugar is consumed, bacteria in the mouth—especially Streptococcus mutans—ferment it and produce acid. This acid lowers the pH level in the mouth, triggering demineralisation and weakening enamel. Over time, the enamel loses its natural protective layer, making teeth more vulnerable, sensitive, and prone to cavities. Without proper dietary control and oral hygiene, cavities can worsen, leading to pain, pulp inflammation, and even tooth loss.
Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Dental plaque is a biofilm of bacteria that forms when sugar and starch residues linger in the mouth. If not removed promptly, plaque hardens into tartar, which adheres firmly to the tooth surface and gums. Tartar not only affects aesthetics but also creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, increasing the risk of gum infections and weakening the tooth roots.
Causes Gingivitis and Periodontal Disease

High sugar levels in the mouth create favourable conditions for bacteria to grow, which leads to gingivitis. Symptoms of gingivitis include swollen, red, and painful gums that bleed easily when brushing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a severe condition that damages the supporting tissues of the teeth, causing bone loss, tooth mobility, and eventually permanent tooth loss. Therefore, limiting sugar intake and maintaining proper oral hygiene is essential.
It increases the risk of dry mouth and bad breath.
Sugar can reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth. Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralising acids, washing away bacteria, and protecting enamel. When salivary levels drop, bacteria multiply easily, breaking down proteins in the mouth and causing an unpleasant odour. Furthermore, a lack of saliva raises the risk of cavities and gum inflammation, worsening oral health if not properly addressed.
Weakens overall dental health
Excessive sugar consumption can impair the body's ability to absorb calcium and phosphate—two essential minerals that help strengthen tooth enamel. A deficiency in these minerals weakens the enamel, making it more susceptible to cracks and damage from external factors. Additionally, sugar increases the risk of gum infections and slows the healing process of gum tissue, leading to tooth looseness and reduced chewing efficiency. As a result, it significantly impacts overall oral health.
A serious impact on overall health
Excessive sugar consumption not only leads to tooth decay and gum inflammation but also poses significant risks to overall health. High sugar intake increases the likelihood of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases by disrupting metabolism and causing insulin resistance. Additionally, a sugar-rich diet weakens the immune system, making the body more vulnerable to infections. Furthermore, as sugar harms oral health, it can accelerate the overall decline of physical well-being.
Preventive Measures Against the Harmful Effects of Sugar on Oral Health

Controlling sugar intake alone is not enough to maintain optimal oral health. It is essential to adopt proper dental care practices to minimise the damage caused by sugar and protect your teeth from harmful bacteria. Below are effective strategies to prevent enamel erosion and maintain strong, healthy teeth:
- Limit sugar consumption, especially refined sugars: Reduce sugar intake by avoiding candies, soft drinks, and processed foods, as they promote the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Brush your teeth properly: Brush at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Replace your toothbrush regularly to ensure effective enamel protection.
- Floss and use mouthwash: Clean between teeth with dental floss to remove trapped food particles and plaque. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to further reduce plaque buildup and prevent cavities.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps rinse away sugar and acids in the mouth, balance pH levels, and lower the risk of plaque formation and tooth decay.
- Consume tooth-friendly foods: Incorporate calcium-rich foods like milk, cheese, and leafy greens, along with crunchy fruits and vegetables that naturally help clean teeth.
- Limit snacking, especially before bedtime: Avoid consuming sugary foods at night, as reduced saliva production during sleep makes teeth more vulnerable to acid attacks.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist every six months for professional cleanings and early detection of issues such as cavities and gum disease.
Sugar is one of the primary causes of oral health problems, including cavities, gingivitis, and periodontal disease. However, by managing your sugar intake and maintaining proper oral hygiene habits, you can effectively protect your teeth. Don't forget to schedule regular check-ups at The East Rose Dental Clinic to ensure optimal oral health!
Services
Working Time
- Monday - Friday: 08:00 - 19:00
- Saturday: 08:00 - 18:00
- Sunday closed
Contact Info
- Hotline 1: 1900 585 874
- Hotline 2: (+84)838 258 778
- Mobile: (+84)908 321 455
- Phone: (+84)2 838 258 778
- info@dentalrose.net
- rosedentalclinicvn@gmail.com
 English
English  Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

